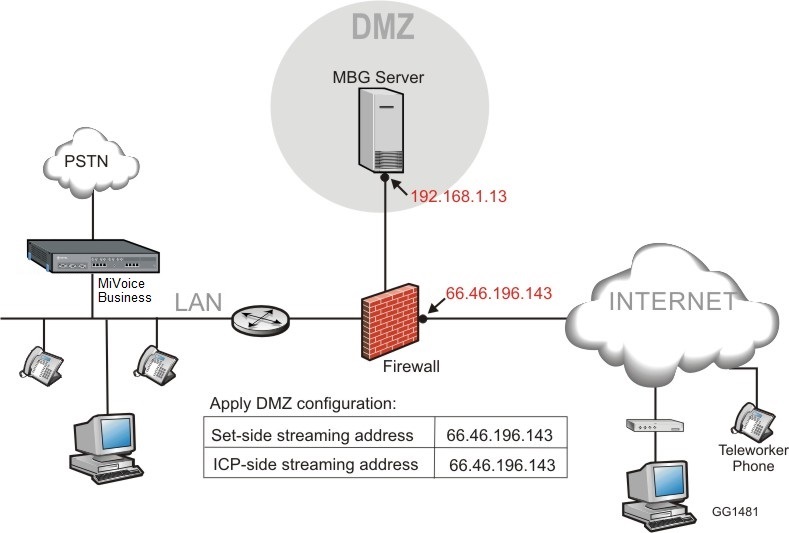
In this configuration, the server is installed in the Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) of a customer’s existing firewall. It acts only as a server and is protected from Internet exposure by the existing firewall.
Note: In a DMZ configuration, the firewall is the gateway for all traffic.
The enterprise firewall must have three network interfaces: WAN, LAN, and DMZ. Two-port firewalls are not supported.
In the firewall's DMZ, allocate a static IP address to the MBG. Typically, this is a private address as defined in RFC 1918.
On the firewall's WAN interface, configure a static IP address from the public/Internet range. This address must be:
dedicated to the MBG solution
publicly routable via the firewall
reachable from the Internet and the internal network
Note: Teleworker devices point to the IP address on the firewall's WAN interface in order to access the MBG server. If this address changes, the Teleworker devices must be updated accordingly.
In MSL, do the following:
Access the MSL Server Console and select Configure this server.
In Local Network Parameters, enter the server's internal (LAN) IP address server or select the default. This address SHOULD be:
dedicated to the MBG solution
private (allocated from DMZ network range)
reachable from the internal network
In MBG, do the following:
On the MBG main page, click the System configuration tab and then click Network profiles.
Select Server-only configuration on the network DMZ.
Select Apply DMZ configuration.
When configuration is complete, the system will use the public, post-NAT address of the server for both the set-side and ICP-side streaming addresses of the MBG. To determine this address, access the MSL Server Manager, select Review Configuration and examine the Internet Visible IP Address field.
The following diagram provides an example of a "Server-only configuration on the network DMZ":
