WebRTC is an API definition drafted by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) that provides browsers and mobile applications with Real-Time Communications (RTC) capabilities. MBG supports WebRTC for browser-based voice and video calling without the need of plug-ins using Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox and Opera on all platforms except iOS.
Platform |
Supported |
Unsupported |
Internet browsers |
|
|
Desktop operating systems |
|
|
Mobile device operating systems |
|
|
Note: WebRTC functionality is unavailable if you connect to the Internet through a firewall that blocks incoming/outgoing UDP packets. Accordingly, if you are using a mobile device, you should connect via the 3G/4G data network or an unrestricted home/office WiFi network. Do not use a public WiFi network for WebRTC calls. |
||
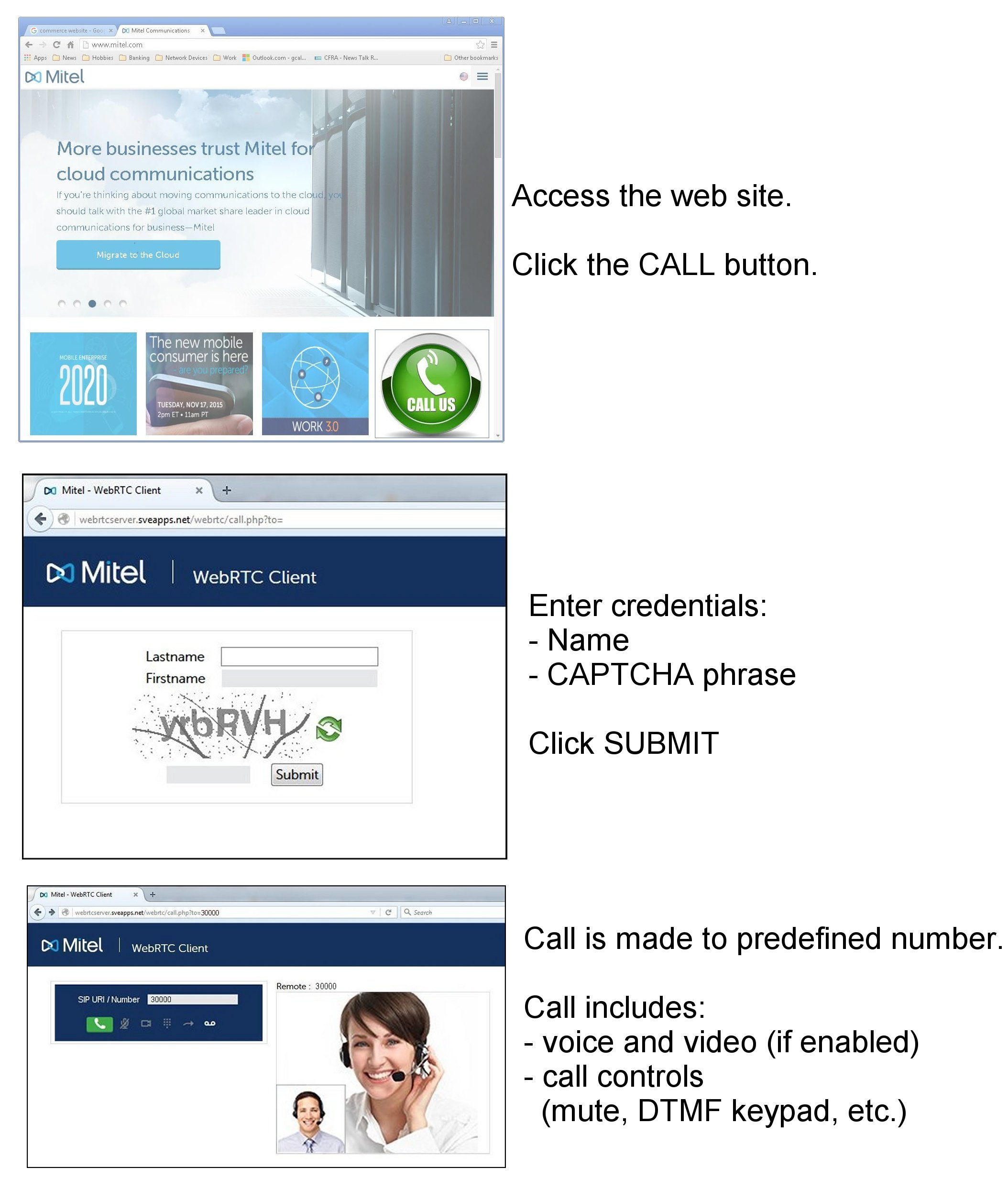
The WebRTC application offers two usage scenarios: "anonymous" and "subscriber" mode.
In this scenario, an external user initiates a call to the enterprise by clicking a button on a web site and then providing minimal credentials (name and CAPTCHA entry). The user, who is known as an "anonymous caller," is directed to an internal service such as a sales or product support hotline configured on an ICP. The administrator, not the anonymous caller, specifies the number for the internal service as part of the WebRTC and web site configuration.
Note: A CAPTCHA entry is a type of challenge-response test used to determine whether or not the user is human.
Once the call is established, an anonymous caller can do the following:
Mute audio/video
Toggle a keypad to send DTMF
Hang up
Enlarge the video to full screen
Toggle the self-view
In this scenario, an external user logs in to MBG from a browser and then registers with an ICP. The user, who is known as a "subscriber," can perform a variety of tasks, including both placing and receiving calls, while registered. The subscriber, not the administrator, specifies the number of the called party.
Note: To initiate registration, the user enters his or her set-side username and password (configured on the SIP Devices screen). MBG then registers the user with an ICP (configured on the ICPs screen). If registration fails, the user can attempt to log in two more times. After the third failure, the user will be prompted to enter a CAPTCHA phrase before being allowed to proceed.
Once registered, a subscriber can do the following:
Mute audio/video*
Toggle a keypad to send DTMF
Accept a call
Receive a call
Hang up
Dial or search in the directory
Enlarge the video to full screen*
Toggle the self-view*
Call voicemail (using a specific button)*
Access the company directory from an LDAP database (if configured)
* Availability of video, voicemail and company director varies by platform.
Example - Subscriber Call with WebRTC client hosted on enterprise web server (requires MiVoice 5000 ICP)
Example - Subscriber Call with WebRTC client hosted on MiCollab web server
The MBG WebRTC gateway is deployed with the WebRTC client, which can be located locally on MBG or on a separate web server. Restrictions apply depending on which call mode and ICP you wish to use. These are outlined in the table, below.
Hosting mode |
Supported Call Modes |
Supported ICPs |
Local server—WebRTC client is hosted on MBG |
Anonymous |
|
Subscriber |
|
|
Separate server—WebRTC client is hosted on a standalone web server |
Anonymous |
|
Subscriber |
|
|
Notes:
|
||
To implement the WebRTC application, complete the following steps:
Configure
ICP for WebRTC
To enable an ICP to receive anonymous calls, you must configure the
ICP with a SIP trunk. Configuration differs depending on which ICP
type you are using, the MiVoice
Business or MiVoice
5000. This procedure is not required if you are only using subscriber
mode.
Configure
MBG for WebRTC
Complete this step for all implementations. As part of this configuration,
you must specify whether you intend to host the WebRTC client on a
standalone web server or on MBG itself.
Configure
Web Server for WebRTC
Perform this step if you are hosting WebRTC client on a standalone
web server with the MiVoice 5000
ICP. It involves downloading the Software Development Kit (SDK) from
the WebRTC on MBG, unzipping the SDK to obtain Javascript libraries
and PHP templates, and then uploading some or all of these files to
your web server. The SDK is provided at no cost but without developer
support. If you require support, you must join the Mitel Solutions
Alliance. See www.mitel.com/msa for details. this procedure is not
required if your implementation does not include the MiVoice 5000 and you do not intend
to host the WebRTC client on a standalone web server.